EHEC infections and haemolytic uremic syndrome in the Oulu University Hospital area in 1995–2016
Background Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) caused by Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia Coli (EHEC) is a leading cause of acute kidney injury and dialysis treatment in children.
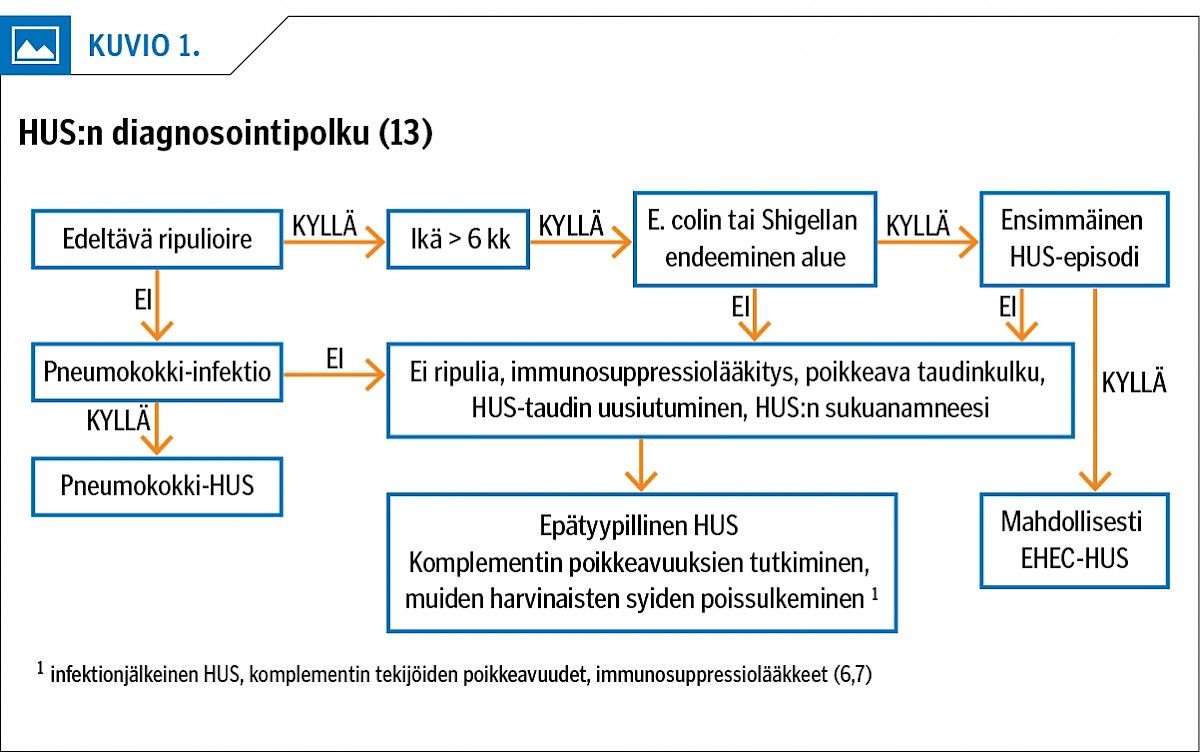
Methods All patients < 18 years of age treated in Oulu University Hospital in 1995–2016 due to EHEC infection or HUS were identified from the hospital data base (ICD-10 diagnosis codes A04.3 (infection caused by EHEC), D59.3 (HUS) and N08.2*D59.3 (renal disease caused by HUS)). Symptoms, laboratory values, treatment and outcomes were analysed.
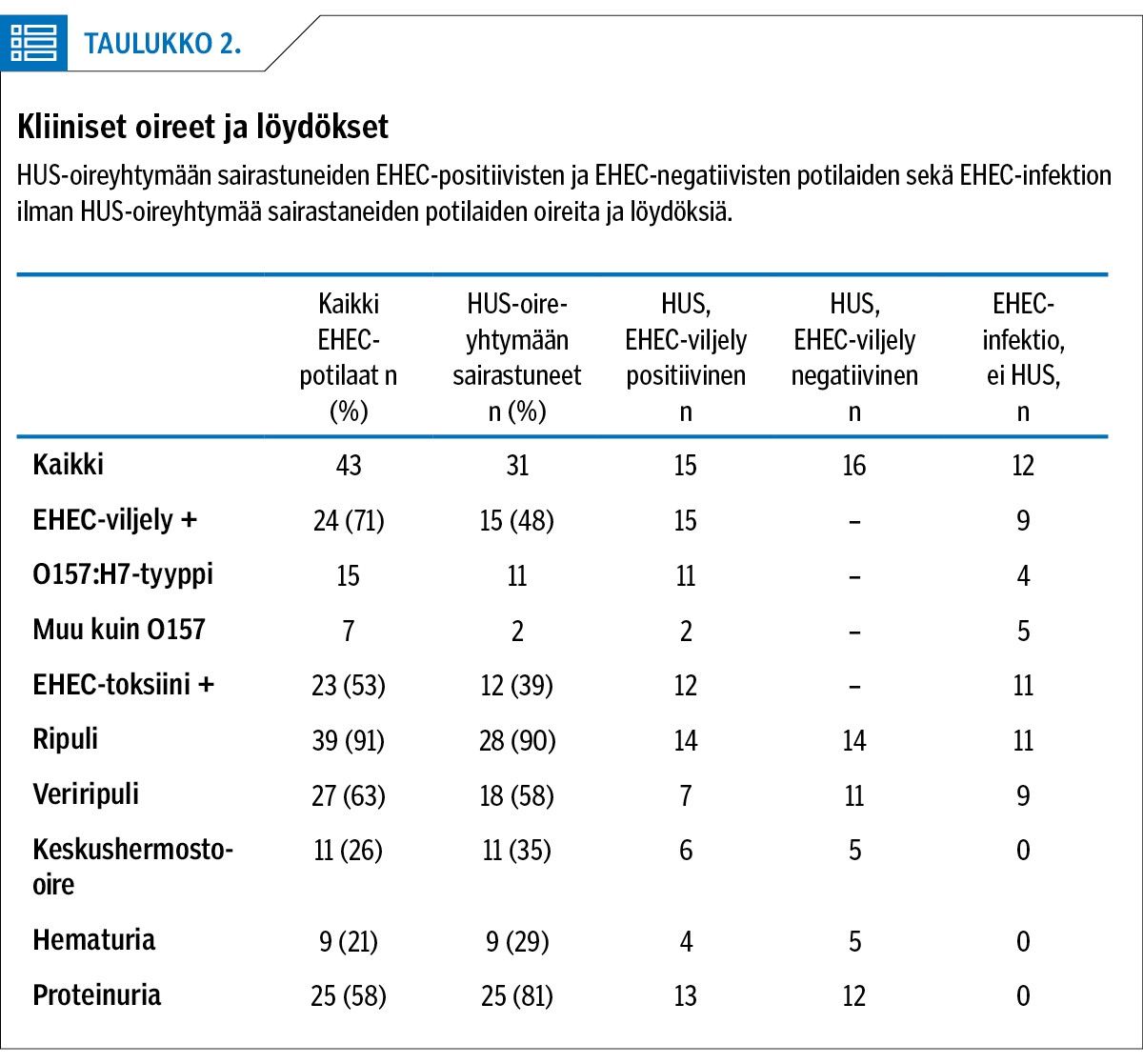
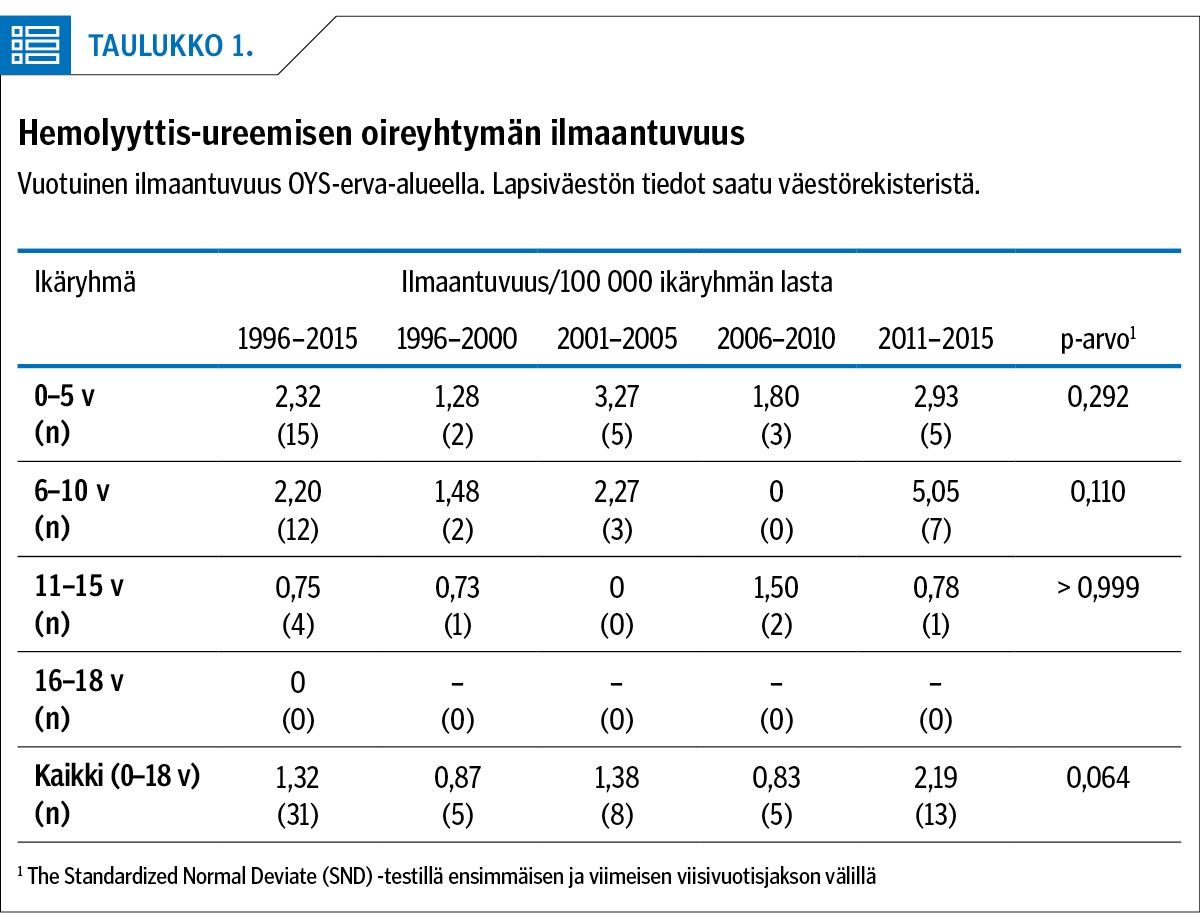
Results A total of 43 children with EHEC infection were found, 31 children with HUS. The incidence of HUS was 1.32/100 000 < 18 years. The incidence of HUS in children < 10 years of age was highest (2.26/100 000) and increased from 1.38 in 1996–2000 to 3.99 in 2011–2015 (P = 0.0505). In total 15 (48%) of HUS patients were found to be EHEC positive; 90% had diarrhoea and 58% bloody diarrhoea. Neurological complications occurred in 11 (9 female) patients. Acute kidney failure was seen in 21 (72%) HUS patients. The need for dialysis was higher (55% vs 100%) (P = 0.008) and the duration of dialysis longer (11.6 days vs 3.8 days) in patients with neurological symptoms.
Conclusions The incidence of HUS is increasing, especially in children < 10 years of age. Early diagnosis of EHEC-HUS may be challenging. Haemoglobin and thrombocyte values, S-creatinine and diuresis should be repeatedly evaluated in order to diagnose HUS early and to start dialysis treatment.