Time to and factors associated with initiation of insulin treatment in people with type 2 diabetes

Background The aim was to determine the time from type 2 diabetes diagnosis to insulin prescription and to study factors associated with insulin initiation among incident type 2 diabetes patients.
Methods Patients with type 2 diabetes diagnosed in 2011–2012 were identified from the electronic health records of the North Karelia Social and Health Services. Factors associated with time to insulin prescription were analyzed with Cox regression models.
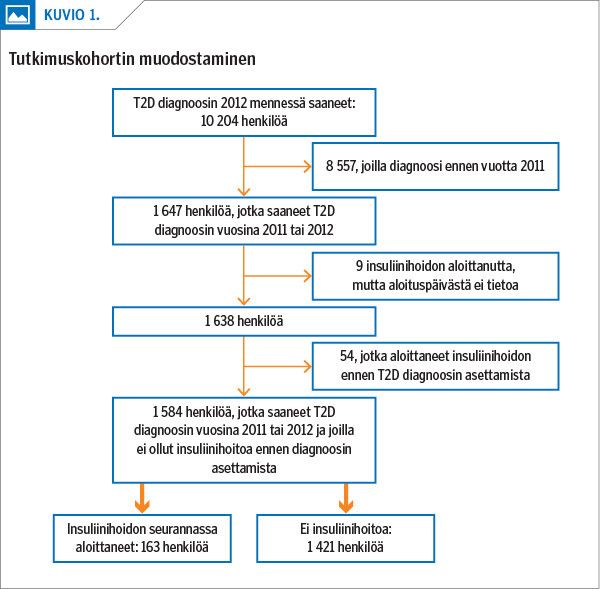
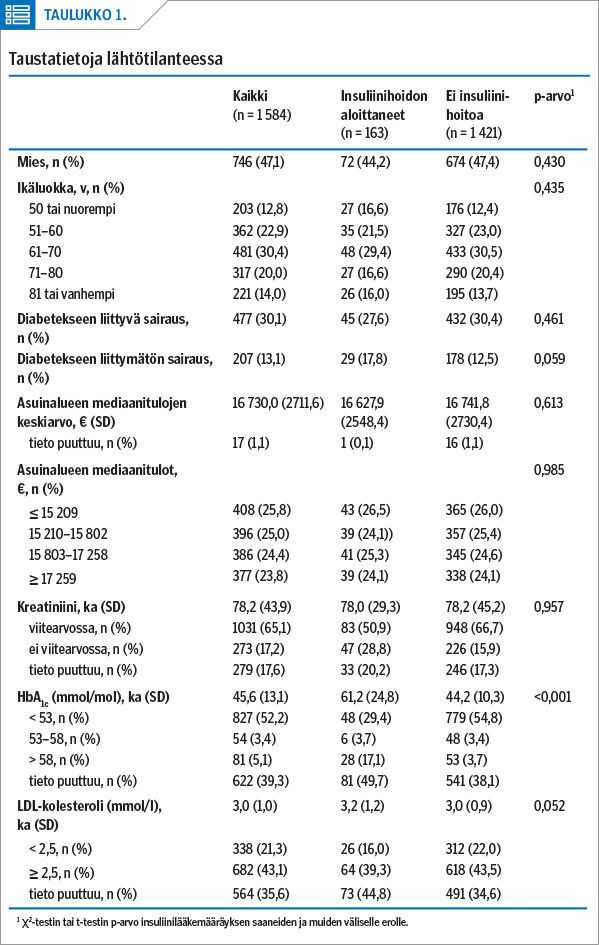
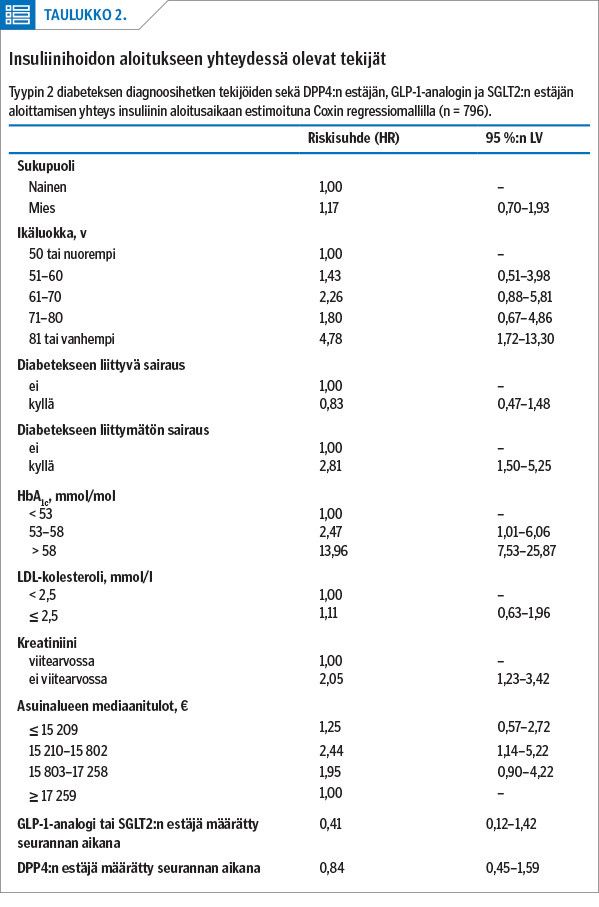
Results Altogether 10.3% (163) of the 1584 North Karelian patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes initiated insulin during the 7 years and 5 months of follow-up. Mean time to onset of treatment was 2.6 (SD 2.0) years from the diagnosis. HbA1c had the strongest association with the initiation of insulin therapy: higher baseline values (> 58 mmol/mol) predicted earlier insulin initiation (HR 13.96; 95% CI 7.53–25.87). People aged 81 years and over were at greater risk (HR 4.78; 95% CI 1.72–13.30) than those aged 50 years or younger.
Conclusions Higher HbA1c and older age increased the probability of earlier prescription of insulin therapy. The results suggest that in all age and population groups in North Karelia treatment of type 2 diabetes is intensified according to age-related individual treatment targets and available treatment options.