Cognition and clients’ participation in RAI assessments

Background Client participation is included in the legislation and quality recommendations for older people care and services. The aim of our study was to explore whether client participation in RAI-assessment is associated with client cognition.
Methods We used data of 53 089 RAI assessments done in 2018 (n = 2 474 operational units). Of the clients, 49% were in home care and 41% in residential care; 69% were female and the average age was 83 years. The average length of care was three years. The Cognitive Performance Scale (CPS 0–6) was used to explore cognition.
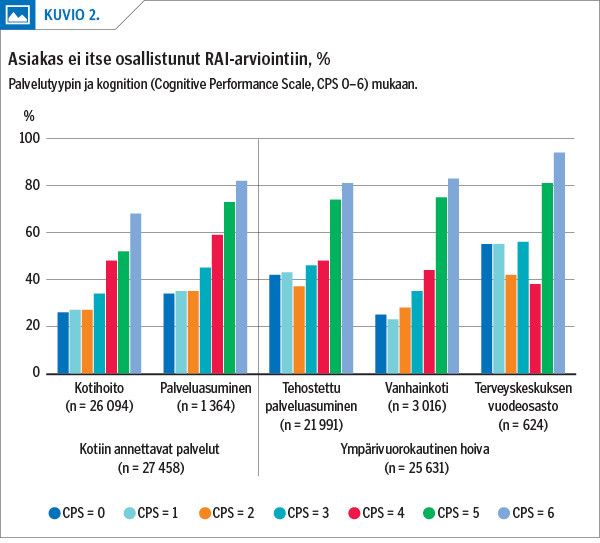
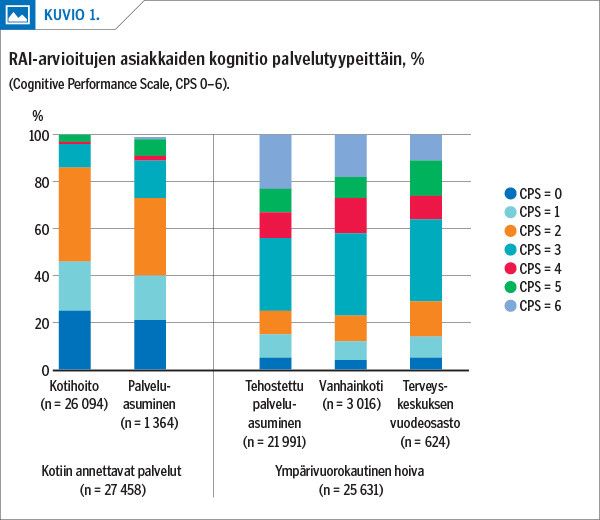
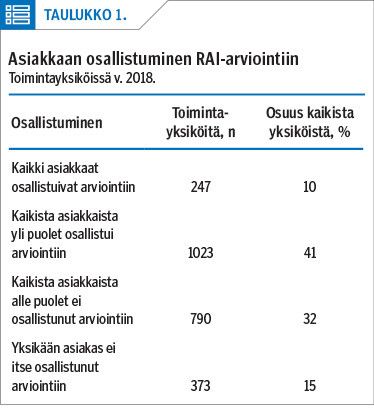
Results Clients’ cognition varied. In half of the clients cognitive impairment was mild to moderate (CPS 2–3) and one in five had moderately severe to very severe impairment (CPS 4–6). Almost half (40%) of the clients did not participate in the RAI assessment. Clients with from intact to mild impairment (CPS 0–2) did not automatically participate, while some of the clients with severe to very severe impairment (CPS 5–6) did participate. Participation was very significantly related (p < 0.0001) to type of service (grouped by the level of services both in home care and in service housing and nursing homes) at each cognition level (CPS = 0–1 / CPS = 2–3 / CPS = 4–6).
Conclusions In the data studied, client participation in RAI assessment did not always relate to clients’ cognition. Participation should be ensured – regardless of clients’ cognitive performance.