Use of oral anticoagulants among patients with atrial fibrillation in 2015–2017 – a register study

Background Anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation has changed in recent years, and there is only limited data on new anticoagulation practices in the treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation in Finland.
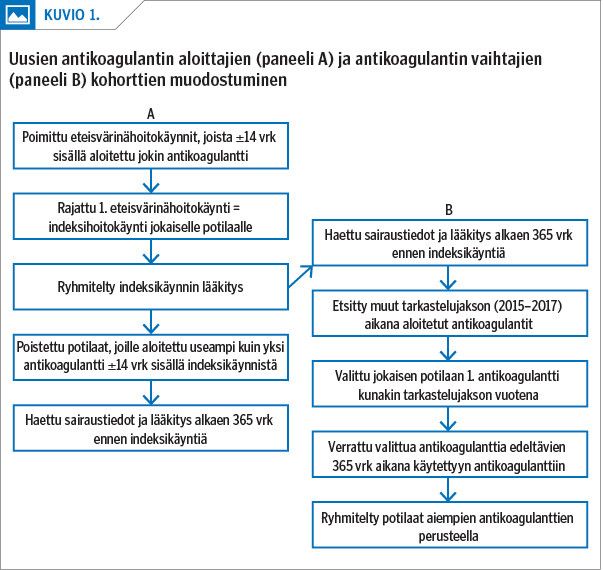
Methods All patients with AF who were in outpatient or hospital care between 2015 and 2017, and their comorbidities by ICD-10 diagnostic codes, were identified from the Care Register for Health Care (Hilmo) of the National Institute for Health and Welfare. The patients’ use of anticoagulants was mapped based on the Register of Primary Health Care Visits (Avohilmo) using Nordic Article Numbers (Vnr).
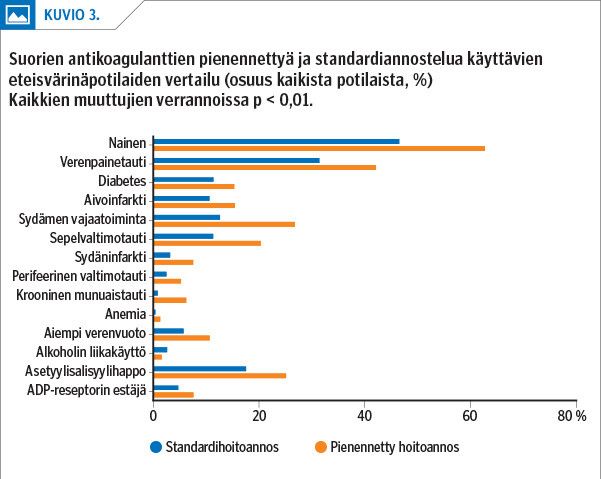
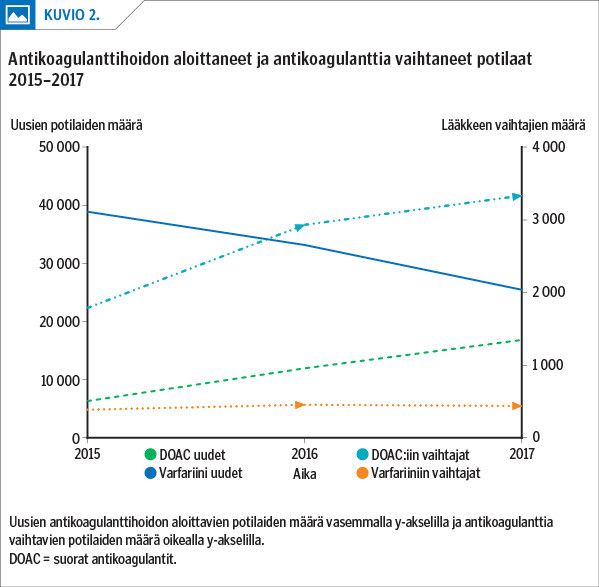
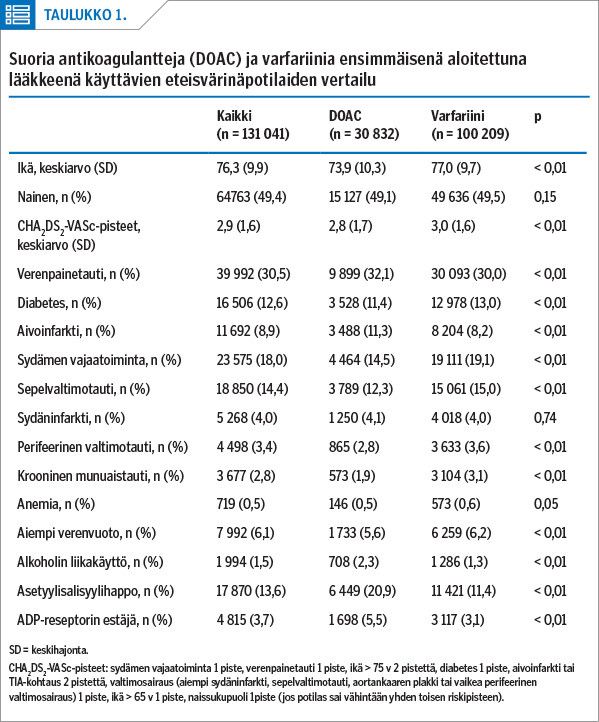
Results During the study period, a total of 100,209 AF patients were using warfarin during the review period as their initial anticoagulant and 30,832 patients were using a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC). Of the AF patients on DOACs 12,433 were on rivaroxaban, 10,229 on apixaban, 7,827 on dabigatran, and 202 on edoxaban. The number of initiated warfarin treatments decreased by 35%, while the number of DOAC treatments increased by 62%. Altogether, 24% of the patients were using reduced-dose DOACs. The patients who were using warfarin were older and more ill than the patients on DOACs. In total, 14% of the patients were using aspirin concomitantly with an anticoagulant.
Conclusions The use of DOACs is becoming more common, while warfarin appears to remain in the treatment of more elderly and comorbid AF patients. Concomitant use of aspirin and an anticoagulant was surprisingly common.