Diverse clinical manifestations, treatment and prognosis of cutaneous vasculitis

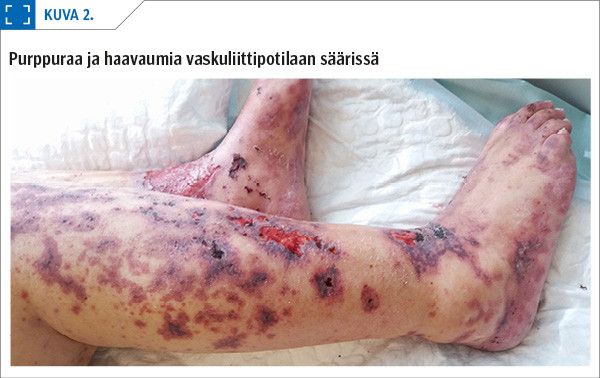
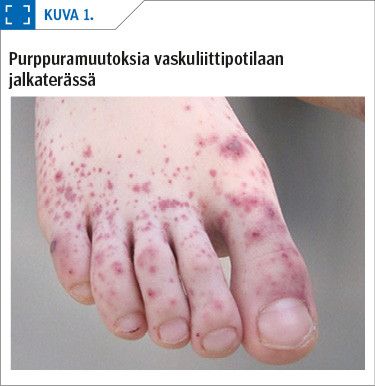
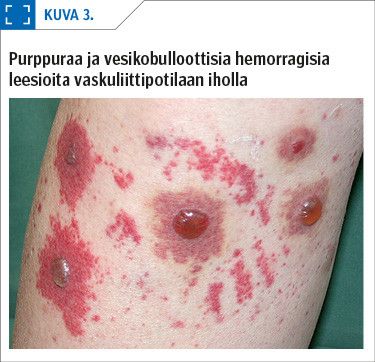
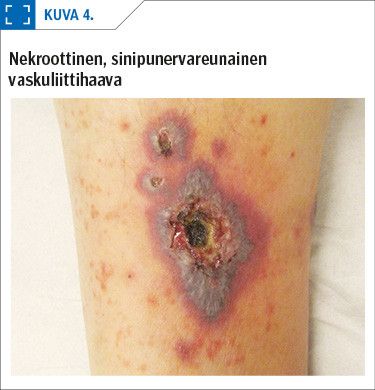
Vasculitis of the skin (cutaneous vasculitis) is defined as inflammatory cell-mediated destruction of the vessels of the skin. Small vessels are predominantly affected (arterioles, capillaries, and venules), but occasionally also medium size arteries. Typical clinical signs of cutaneous vasculitis include purpura, livedo racemosa and urticaria; moreover, destruction of the vessel walls and subsequent ischaemia can result in the development of necrosis and an ulcer.
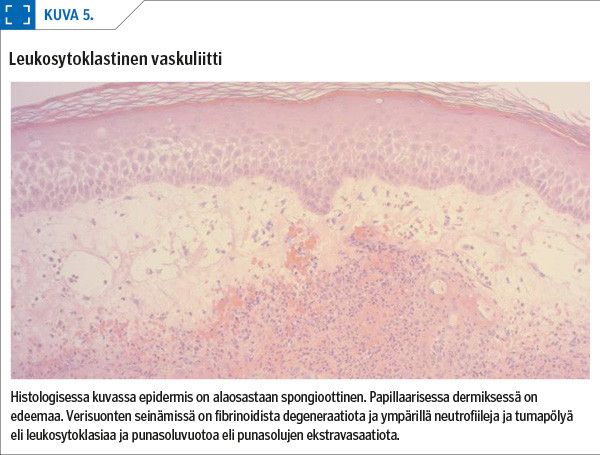
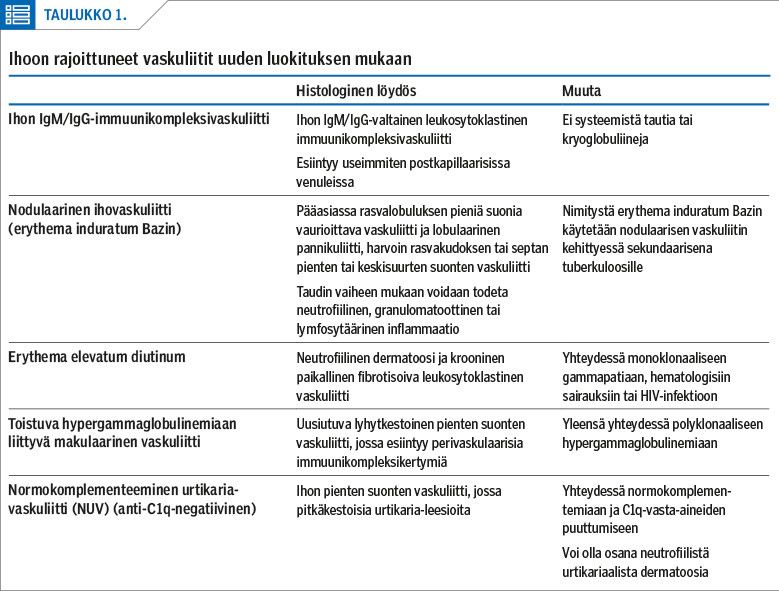
Diagnosis of cutaneous vasculitis should be confirmed by histopathological analysis, and the aetiology of the vasculitis and the possibility of the presence of systemic disease should be assessed. Mild vasculitis of the skin without evidence of systemic disease may improve even without treatment, whereas patients with vasculitic ulcers should be treated by dermatologists specialized in the treatment of atypical ulcers. Often a multidisciplinary team is also needed. The treatment should be tailored individually taking into an account the aetiology of the vasculitis, the patient’s comorbidities, other medications and the severity of the cutaneous manifestations.
The prognosis of cutaneous vasculitis varies and is dependent on the manifestation, aetiology and severity of this disease. Most patients diagnosed as having cutaneous vasculitis have mild and self-limiting disease, but cutaneous vasculitis may also lead to amputation of a limb or at worst even to death. Disease recurrences can also occur.