Prediabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases; does it also increase the costs of treatment?

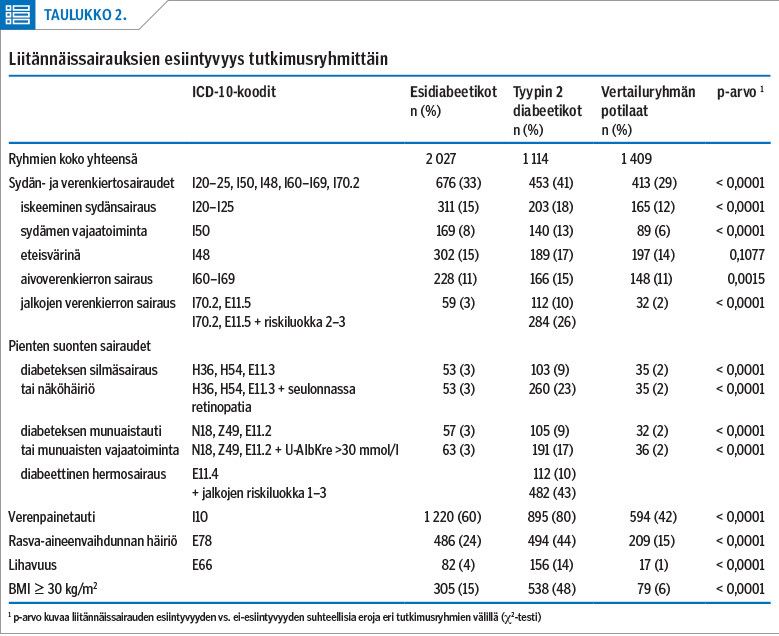
Background According to population surveys, there are more patients at increased risk of type 2 diabetes than there are type 2 diabetics and, notably, these patients have a markedly increased risk of developing not only type 2 diabetes but also cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, the costs of treatment caused by type 2 diabetes and its comorbidities are extremely high.
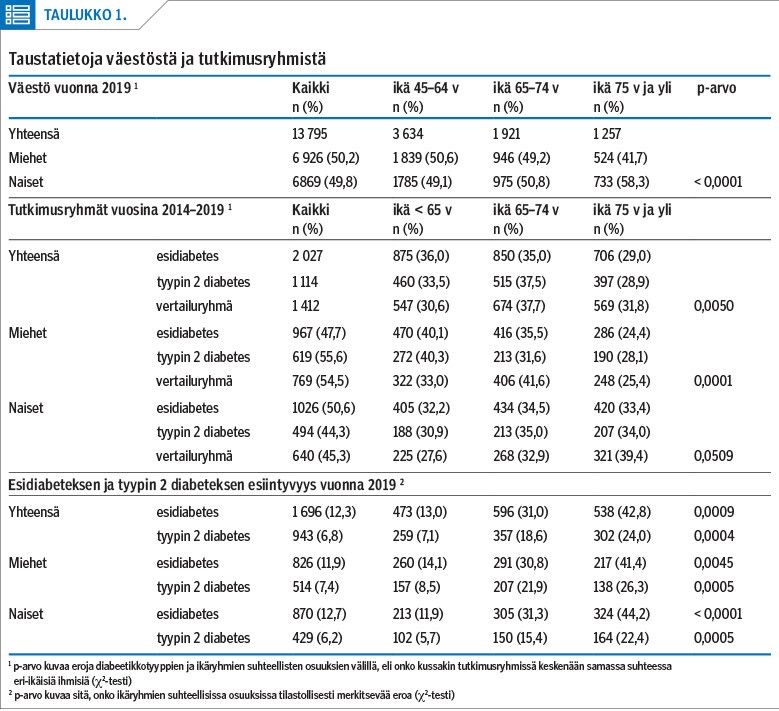
Methods Prediabetics were identified from the patient register of the health centre based on abnormal glucose metabolism. Their treatment, the number of comorbidities, and the costs of treatment were compared with those of type 2 diabetics and control patients of the same area.
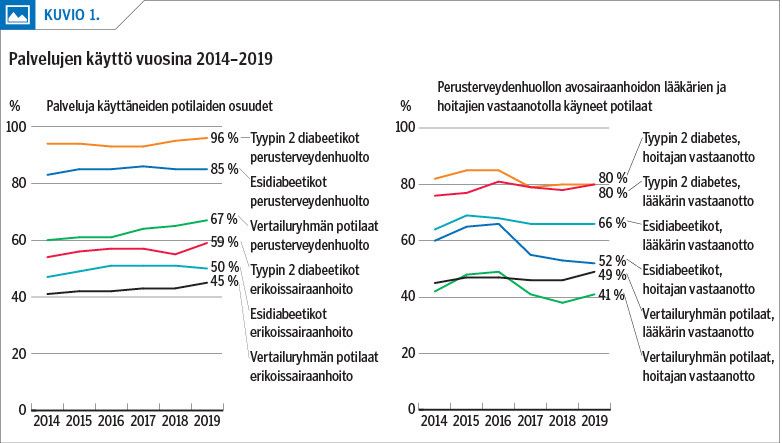
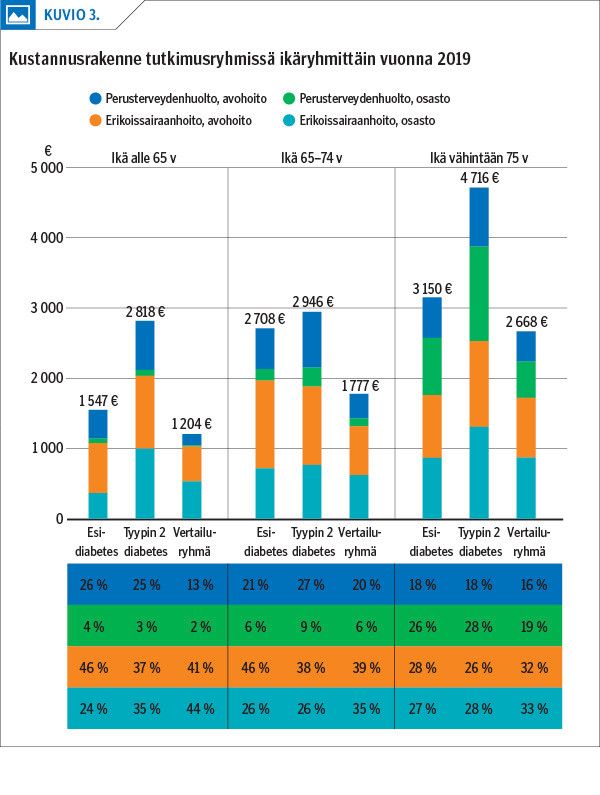
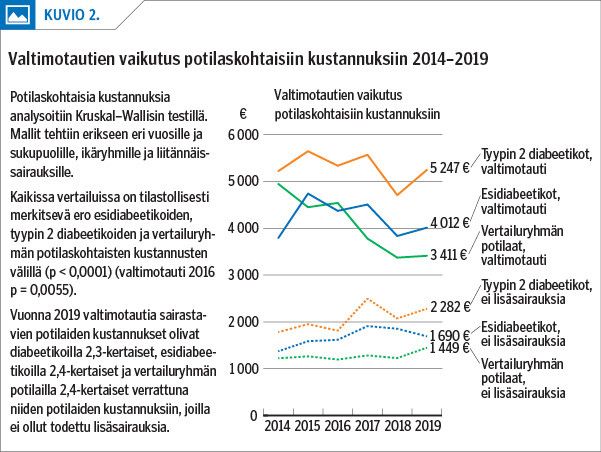
Results The prevalence of prediabetes was almost double that of type 2 diabetes in all age groups. The prevalence of comorbidities and additional costs per patient were higher in prediabetics than in the control group, but lower than in type 2 diabetics in almost all diagnosis groups.
Conclusions Prediabetes and its comorbidities increased the costs of treatment compared to the situation when glucose metabolism remains normal. The total costs of public health care were found to be even higher in prediabetics than in type 2 diabetics and they were largely due to the specialist care. The intensity and follow-up of treatment were lower in prediabetics than in type 2 diabetics.